Week 05 - Communication Skills
A presentation at Heritage University in September 2019 by Jacob Campbell and is tagged with Heritage University, BASW Program, SOWK 486w
Description
Week five focuses on communication skills that we use as clinicians. The agenda is as follows:
- The Facilitative conditions
- Empathy
- Authenticity
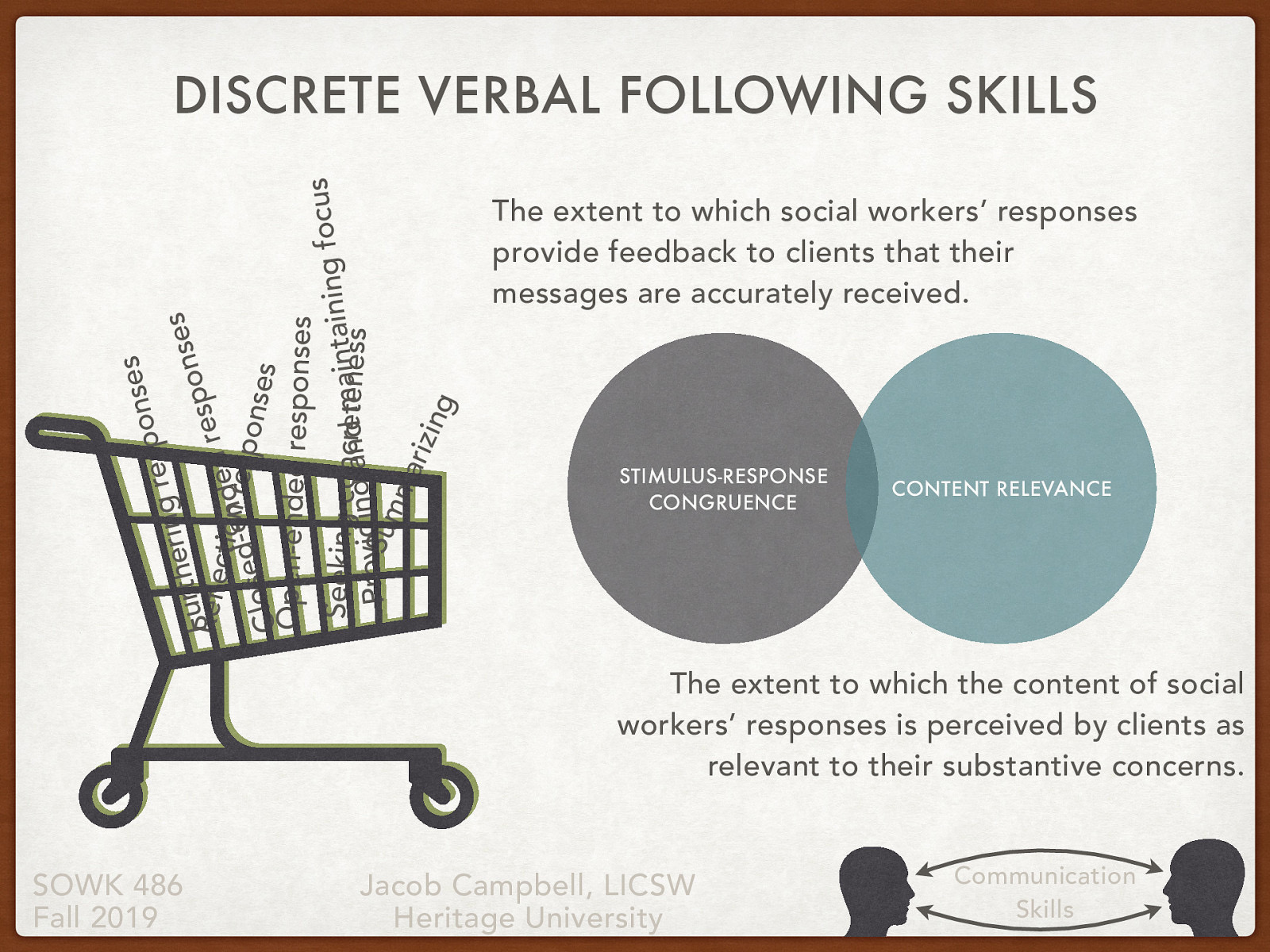
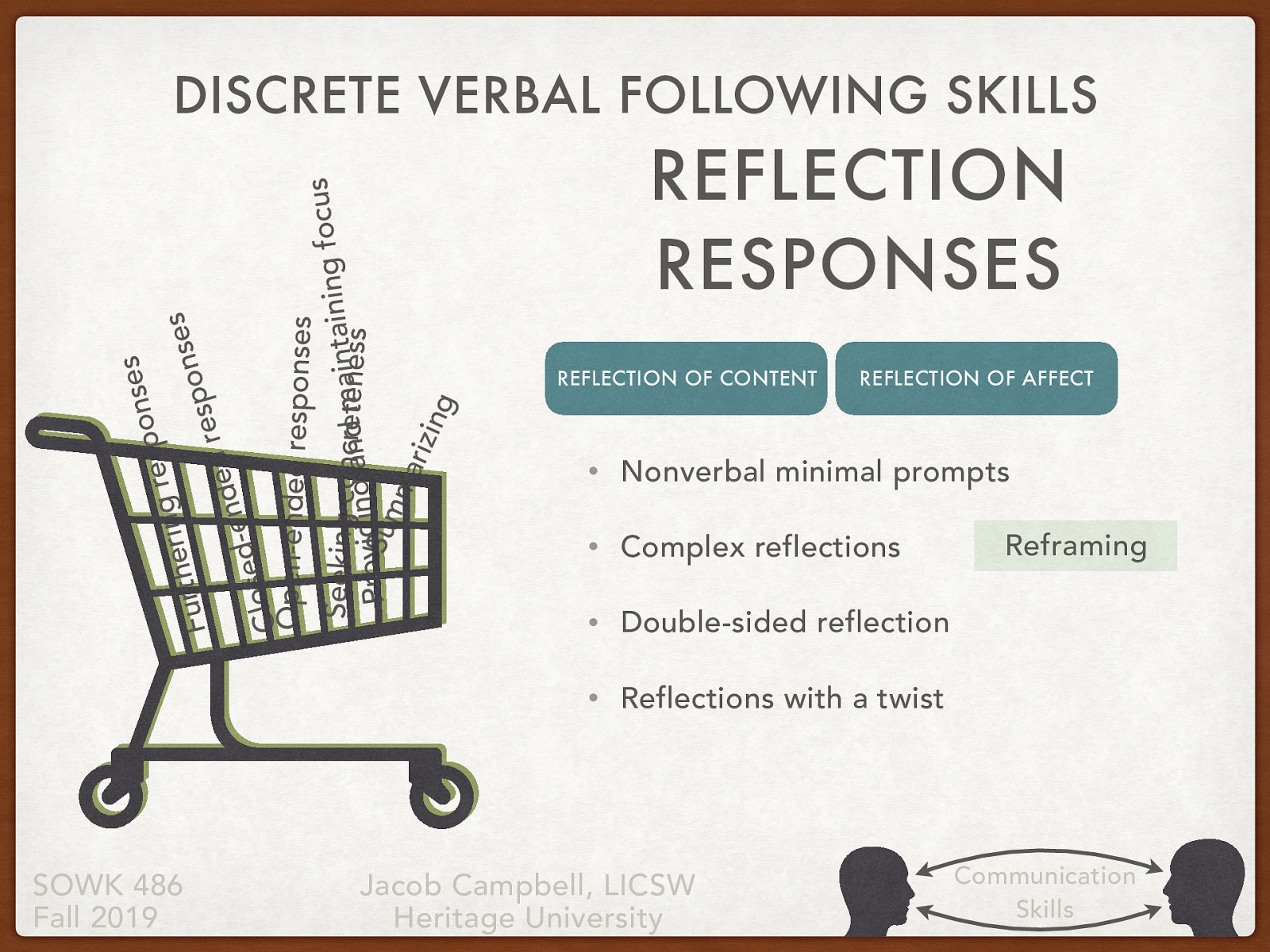
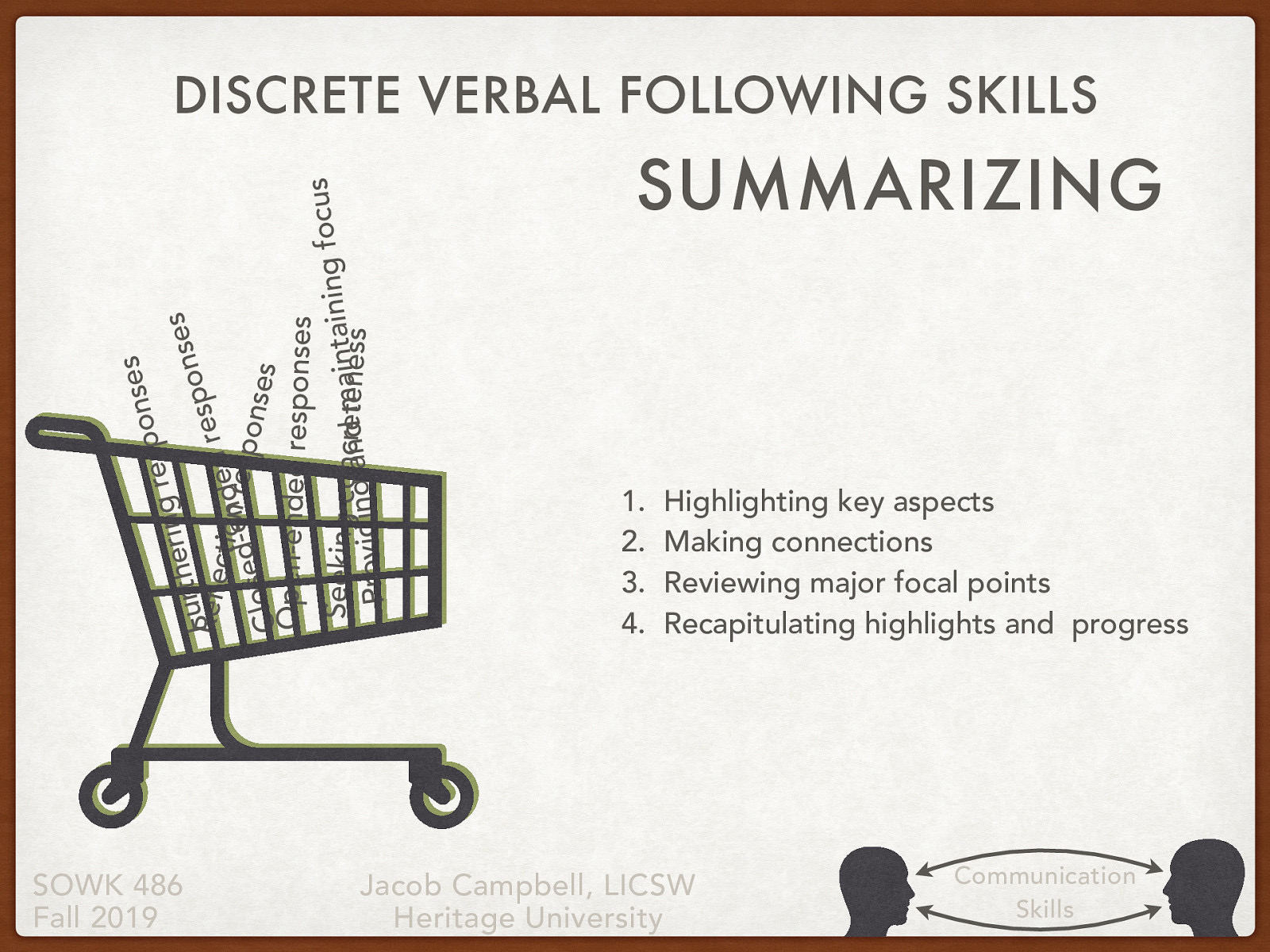
- Discrete verbal following skills


![“Clients often have an unclear idea about what to expect from contact with a social worker, and those ideas may differ from the social worker’s expectations as well (Kadushin & Kadushin, 1997). This is most evident when the client has been referred or mandated for service. Clarifying expectations becomes a key intervention in work with clients who have not chosen to see a social worker (Rooney et al., 2009; Trotter, 2006).” Determine your client expectations: Ask questions to determine what their expectations. Help them to manage unrealistic or unreasonable expectations. Emphasize client responsibility: What are the expectations that you or others have on them. Emphasize difficulties inherent in the process: Making change is hard. Extinction burst. Clarify your own role: What will you be doing and expectations they can have on you [Small Group Activity] Have students break up into their partner group for an assignment from another class. Have them go though and help clarify roles for the assignment. B. F. Skinner (1933) “Resistance to Extinction” in the Process of Conditioning, The Journal of General Psychology, 9:2, 420-429, DOI: 10.1080/00221309.1933.9920945](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-3.jpeg)

![Carl Rodgers and person Center Counseling probably give the best and most focus on basic helping attitudes. The facilitative conditions (or core conditions) in helping relationships were originally denoted by Carl Rogers (1957) as… Empathy Unconditional positive regard Congruence Much of the current research describes these as: Warmth Authenticity Empathy Facilitative conditions are often thought to be the foundation-level skills that undergird many treatment models and help create a positive client–social worker relationship. Research has especially supported the correlation of empathy with positive social work outcomes. The facilitative skills are particularly useful in treatment situations with voluntary clients. [Discussion] What words would you choose as antonyms for each of these? [Activity] Have everybody pair up with a partner. Each group will receive one of the three words listed above or it’s antonym. You will have a couple of minutes to think about a scenario and act it out in front of the class. The class will guess what helping (or not helping attitude is being portrayed).](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-5.jpeg)
![The RSA. (2013, December 10). Brené Brown on Empathy. Brené Brown on Empathy. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Evwgu369Jw The following is a short video clip from a presentation that Brené Brown did called the “The Power of Vulnerability.” [Activity] Watch the video clip. [Discussion] What did you think of Theresa Wiseman (2007) concept of four parts to empathy. “Toward a holistic conceptualization of empathy for nursing practice.” Perspective taking and recognizing their perspective as truth Staying out of judgment Recognizing emotion in other people Communicating emotion with people [Discussion] What do you think about this video?](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-6.jpeg)


![You feel __ about __ because __ You feel __, yet you also feel __ [Partner Group Activity] With partner, take turns sharing respectively for about five minutes, about an experience that they experienced a emotional response (any emotion, happiness, sadness, excitement, nervousness, etc. - does not need to be an overly personal story.) The person not telling the story job is to draw out the details of the event and find opportunities to respond empathetically.](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-9.jpeg)


![[Whole Class Activity] What is authenticity and why is it important? Authenticity is defined as the sharing of self by relating in a natural, sincere, spontaneous, open, and genuine manner.](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-12.jpeg)

![Ragan, T. (2014 Jan 30) Carol Dweck - A study on praise and mindsets [Video File]. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/NWv1VdDeoRY. [Whole Class Activity] Watch the video. [Whole Class Activity] Discuss: How does this impact us as social workers How do we give specific praise](https://presentations.jacobrcampbell.com/QPyNUU/deck-3609-large-15.jpeg)