SOWK 487 - Week 07 - Group Practice Models - Cognitive Behavioral Group Work
A presentation at Heritage University @ CBC Week 07 in in Pasco, WA 99301, USA by Jacob Campbell

SOWK 487 Spring 2021 Planning: Class 07
Time: Wednesday’s from 5:30-8:15
Date: 02/24/21
Content: Cognitive Behavioral Group Work
Reading Assignment: Garvin et al. (2017) Chapter 8
Due Dates:
- A-01: Synchronous Class Engagement Attend class
- A-02: Asynchronous Class Engagement Thinking errors teach back video with an initial post due Friday 02/26/21 at 11:55 PM and two replies due Sunday 02/28/21 at 11:55 PM via My Heritage Class Forums
- A-03a: Family Treatment Modality Research Paperdue Sunday 02/28/21 at 11:55 PM via My Heritage Assignments
- Read Garvin et al. (2017) Chapter 8

Mindfulness minute
[Whole Class Activity] Have the class go through and walk them through breathing activity.

Agenda
- Curriculum used with cognitive-behavioral group work
- Phases of the group process
- Implementation of a group
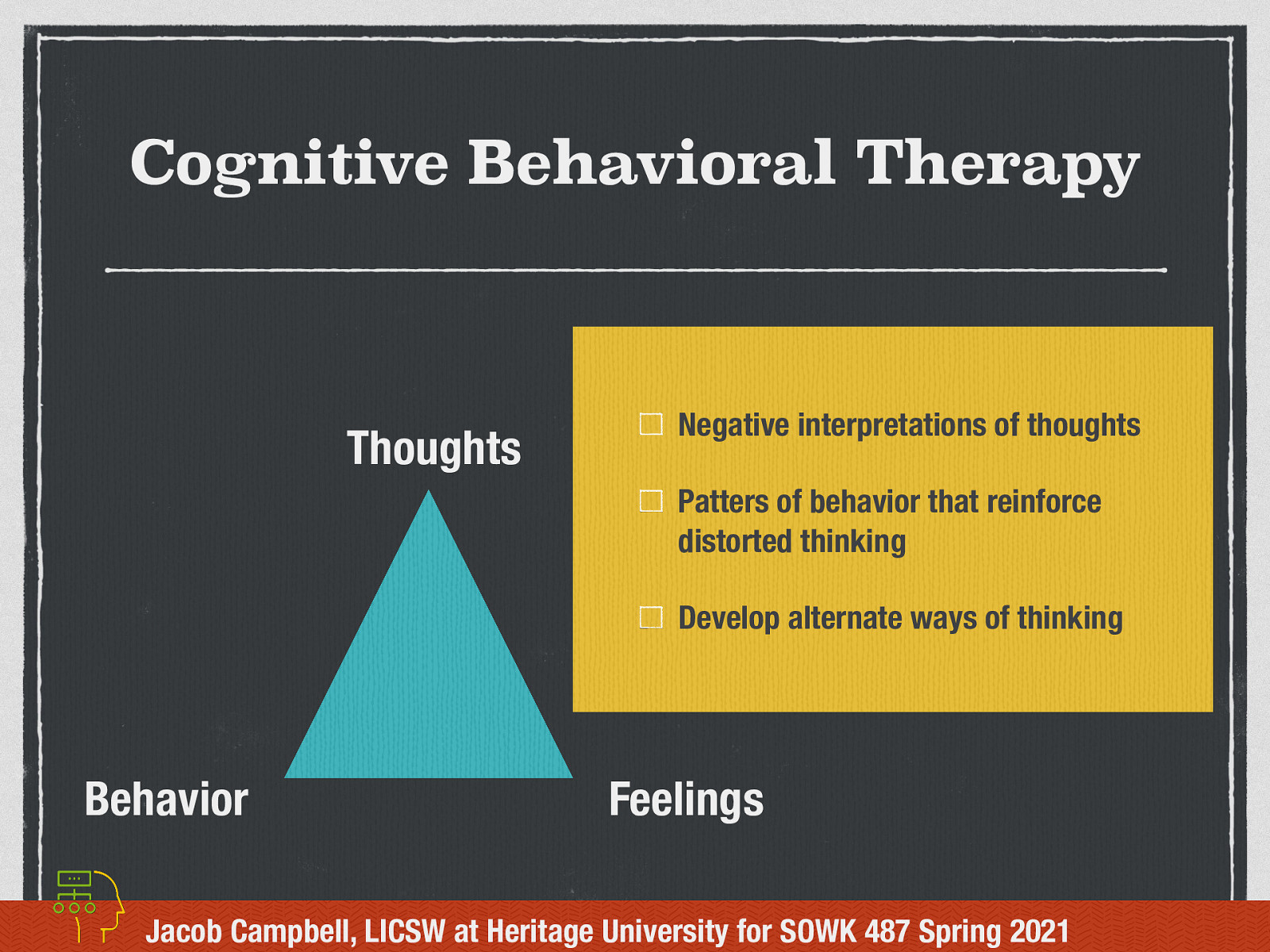
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (Individualized)
To start off our conversation about Cognitive-Behavioral Group Work, I thought that it would be helpful to discuss what is Cognitive behavioral therapy— CBT, a therapeutic approach which can help people with a wide range of mental health problems.
CBT is based on the idea that how we think (cognition), how we feel (emotion) and how we act (behavior) all interact together. Specifically, our thoughts determine our feelings and our behavior. This is sometimes referred to as the cognitive triangle.
- Bring awareness to negative interpretations of thoughts
- Review patters of behavior that reinforce distorted thinking
- Develop alternate ways of thinking

Cognitive-Behavioral Group Work
Cognitive-behavioral group work (CBGW) is one of the most widely implemented treatment group approach. It is used to treat a wide range of services.

Example Group Curricula
It might be helpful to see what some examples of group curriculum might be. While I would say that all of these curricula fall in the category of a Cognitive Behavioral Framework, they aren’t necessary 100% Cognitive-behavioral group work…
[Whole Class Activity] Spend time discussing each of the curricula and providing an overview.
[Whole Class Activity] Have the class break up into three groups. Each group will have an opportunity to read through the curriculum from the three sources:
- Guiding Good Choices Curriculum
- Dragon Slayers’ Curriculum
- Why Try Curriculum
Consider discussion regarding the following:
- What stands out to you about the curriculum
- How are they the same or different
- How facilitated is each of the different curricula
[Whole Class Activity] Discuss what they saw in the curriculum, what stood out… etc.
- [ ] Print out 01 copy of Dragon Slayers’ Curriculum
- [ ] Print out 01 copy of Why Try Curriculum
- [ ] Bring a copy of the curriculum for Guiding Good Choices Curriculum

Therapeutic Procedures
There are some therapeutic procedures which are either unavailable or less efficient for individual treatment and are often implemented when doing CBGW.
- The Buddy System: having a partner to learn new skills
- Group Exercises: Think about curriculum
- Multiple Modeling: ART as an example and multiple role plays
- Group Feedback: getting feedback from peers is sometimes more powerful than from a professional. Think about Drug and Alcohol groups and peoples BS detectors.
- Group Brainstorming: Both to solve individual and group problems.
- Mutual Reinforcement: Similar benefits as the mutual aid model.
Some of the therapeutic procedures which are implemented in doing individual CBT can also be used in CBGW.

Phases of Cognitive-Behavioral Group Work
The phases identified for CBGW are as follows:
- Beginning the Group
- Motivational Enhancement Phase
- Assessment Phase
- Intervention Phase
- Generalization Phase
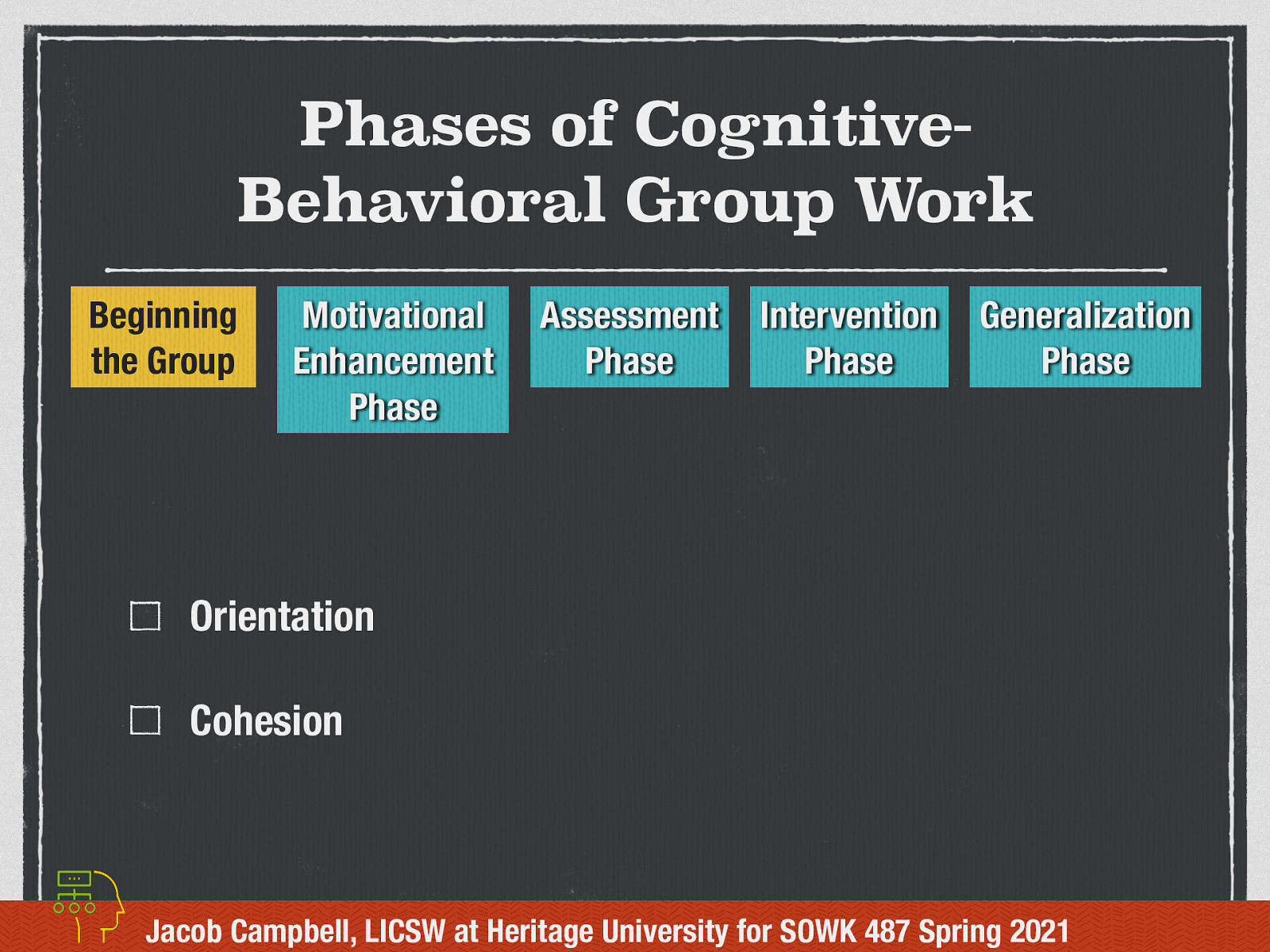
Beginning the Group
All groups have a beginning of the group phase. In the beginning of the group phase for CBGW, there are a couple of tasks that we think about in this phase.
- Orientation - What are ways that we can provide an orientation for clients in a group?
- Cohesion - the mutual liking of members for each other and the group worker and their attraction to the program of the group.

Motivational Enhancement Phase
Generally in a CBGW there will be time that the worker focuses on increasing the motivation of the participants. This might mean addressing ambivalent or negative views of the group. These can look like…
[Whole Class Activity] Talk about possible strategies and ways of addressing these as a reflective exercise.
- Reluctance to speak
- Anger about being in treatment
- Denial of any serious problems
- Setting themselves apart
- Speaking only to the group worker
- Unwilling to provide self-disclosure
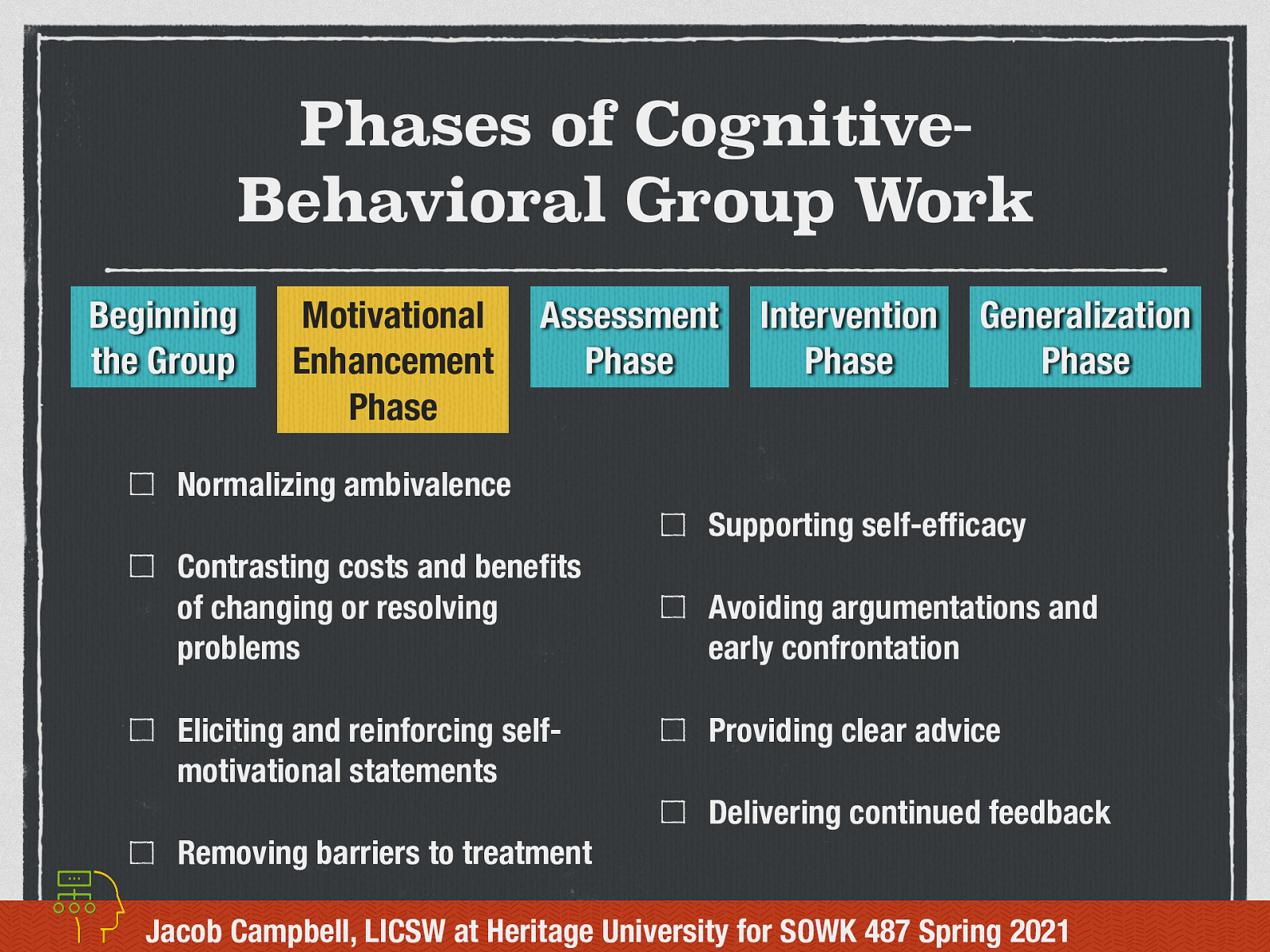
Motivational Enhancement Phase (2 of 2)
Some common processes in enhancing motivation include…
- Normalizing ambivalence
- Contrasting costs and benefits of changing or resolving problems
- Eliciting and reinforcing self-motivational statements
- Removing barriers to treatment
- Supporting self-efficacy
- Avoiding argumentations and early confrontation
- Providing clear advice
- Delivering continued feedback
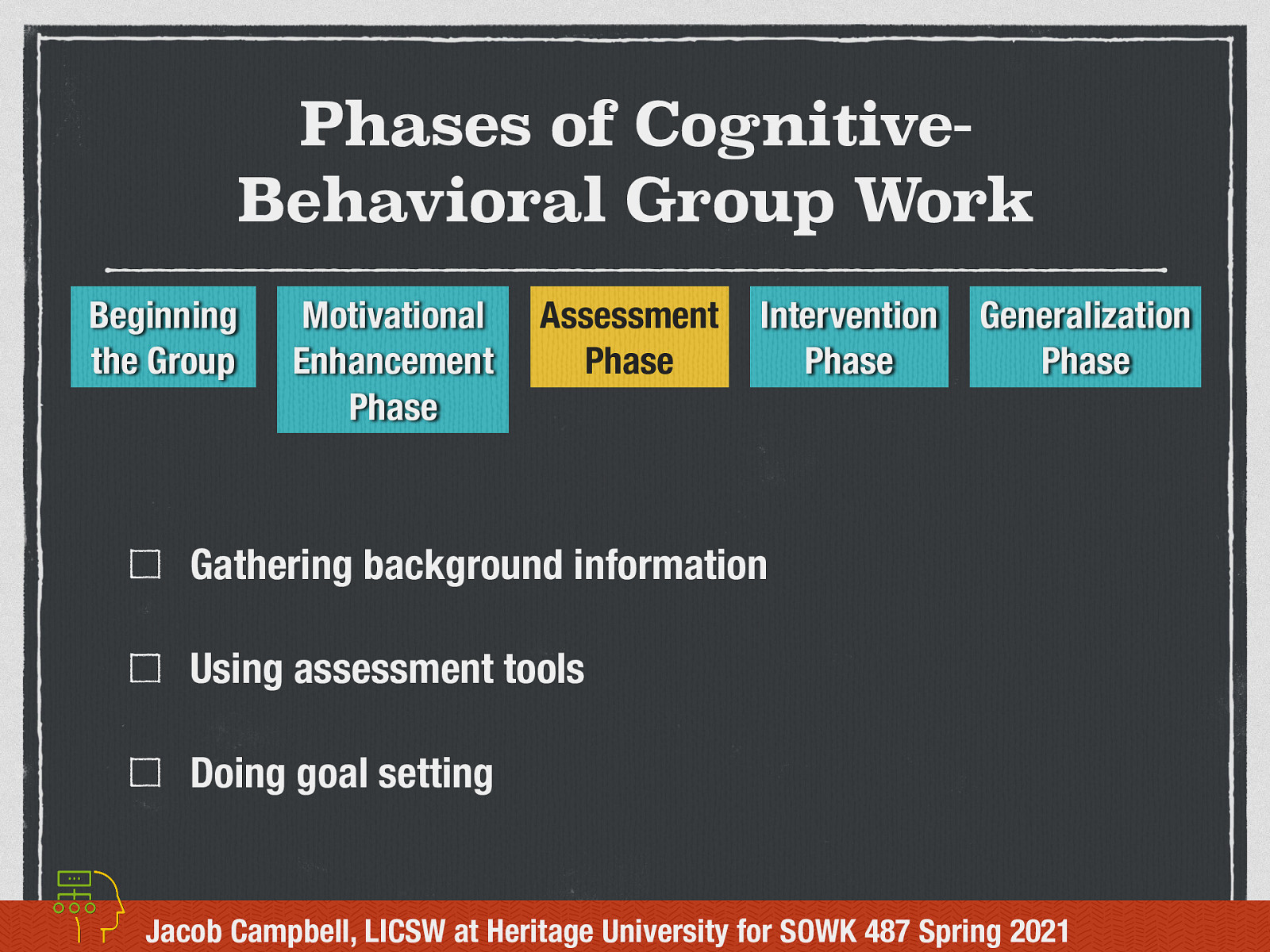
Assessment Phase
In the assessment phase it might take place before the group or in the orientation phase as well as throughout the group process. In this phase the worker is:
- Gathering background information: Before, at the beginning or during
- Using assessment tools: think screeners
- Doing goal setting: both individual and common treatment goals.
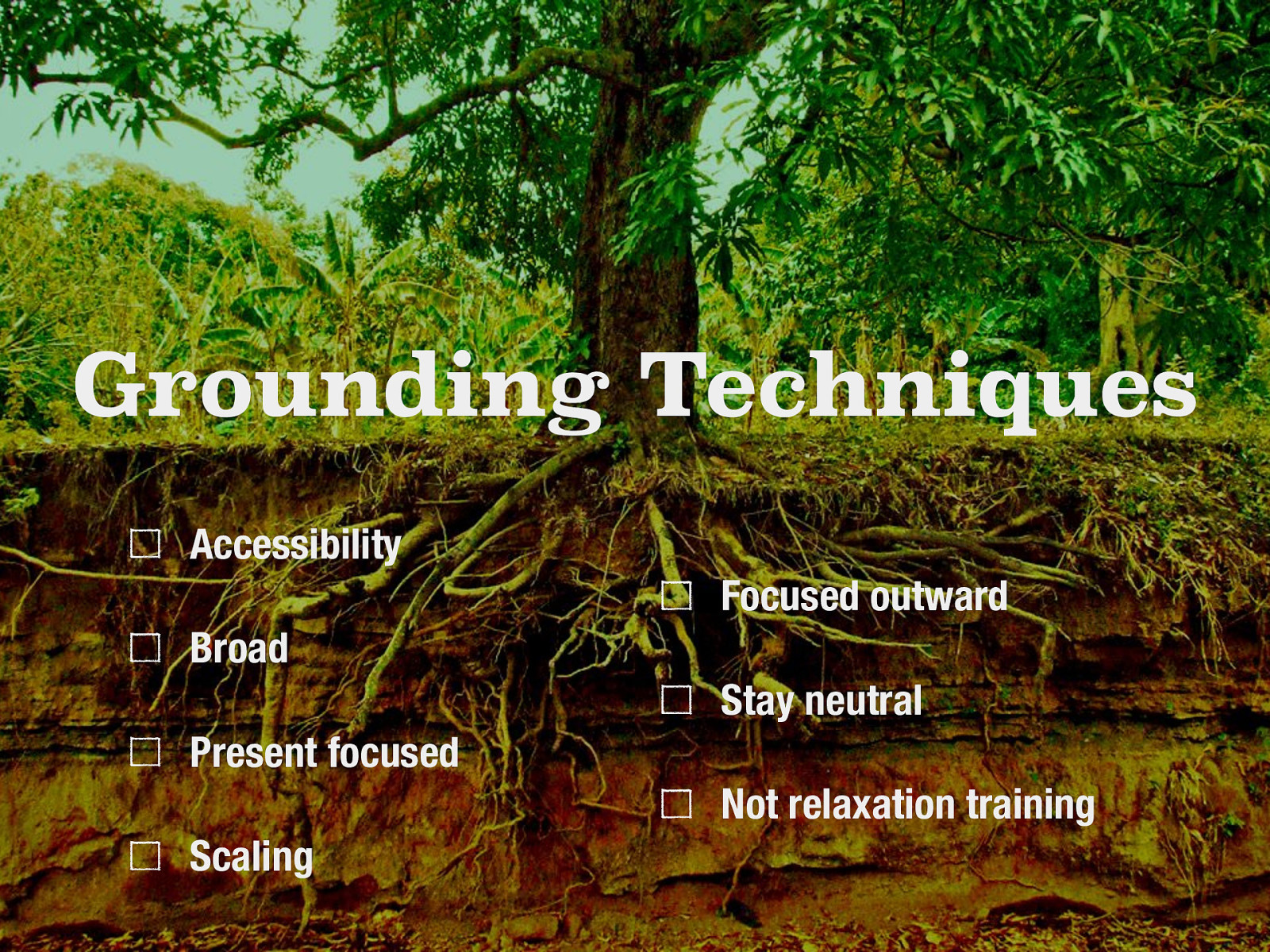
Grounding Techniques
I want to share with all of you a tool that that I have often taught to clients. Grounding is a set of simple strategies to detach from emotional pain. To be grounding, it should fall under the following guidelines…
- Accessibility: do it at any time, any place, anywhere, and no one has to know.
- Broad: put a healthy distance between you and negative feelings (useful for when faced with a trigger, enraged, dissociating, having a substance craving).
- Present Focused: keep your eyes open, scan the room, and turn the lights on to stay in touch with the present. Do not focus on the past or the future.
- Scaling: scale your emotions when using grounding. Rate at your emotion (craving, impulse… etc) on a scale from 0-10 before beginning grounding. After implementing your grounding technique, rate your emotion again.
- Focus Outward: Do not talk, think, or journal about your feelings. The purpose of grounding is to distract away from negative feelings, not get in touch with them.
- Stay Neutral: avoid judgments of good and bad.
- Not Relaxation Training: note that grounding is not the same as relaxation training. Grounding is more active, focuses on distraction strategies, and is intended to help extreme negative feelings.
[Whole Class Activity] Review the sheet. Practice some of the skills / discuss them. Talk about how it can be implemented in a group format (in part or whole)
[ ] Print 24 copy of Using Grounding To Detach From Emotional Pain handout
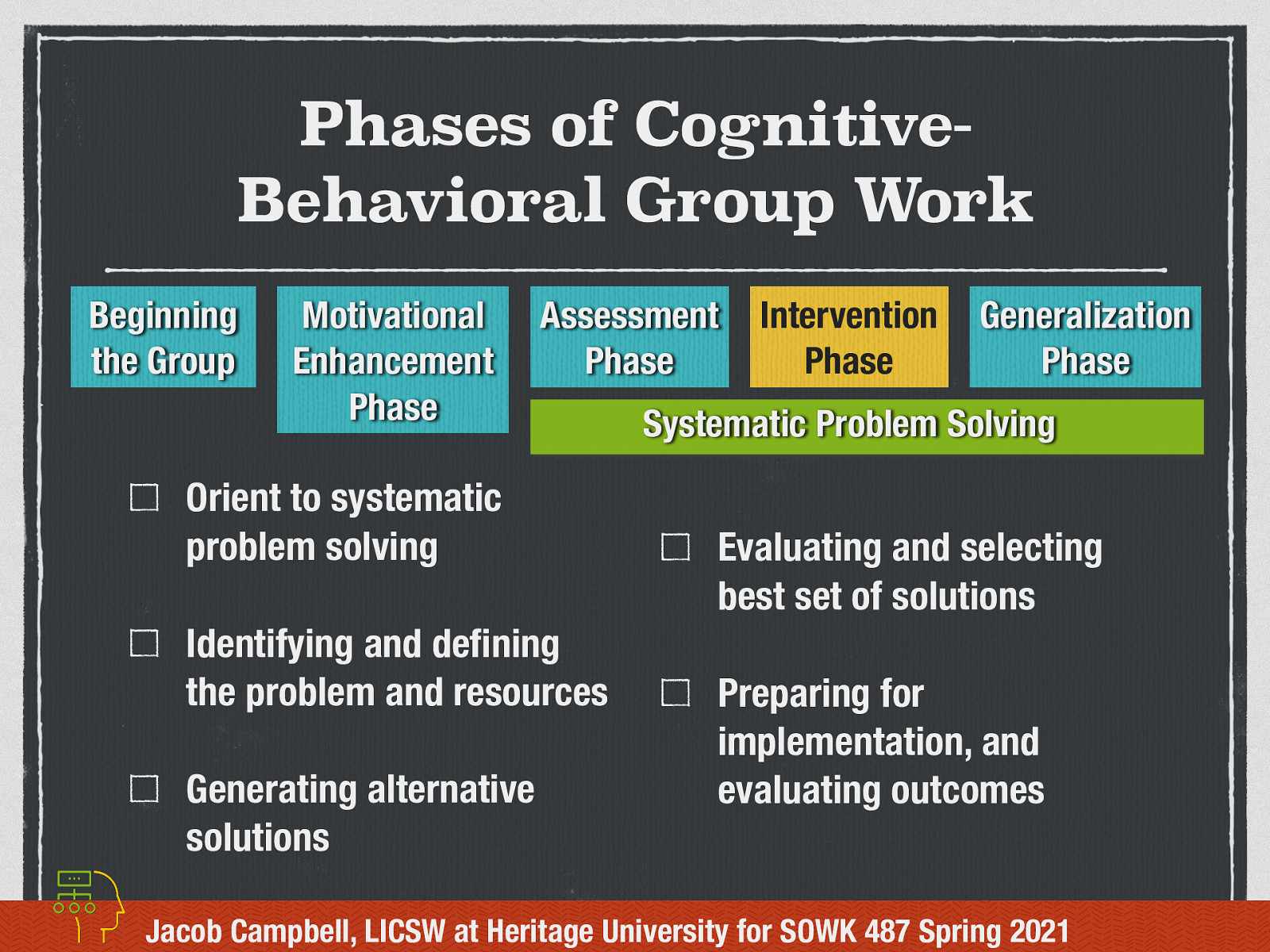
Intervention Phase - Systematic Problem Solving
CBGW encompasses a number of different types of interventions that can be implemented. One of these is…
Systematic Problem Solving is where concerns brought to the group and discussed with the group usually includes:
- Orient to systematic problem solving
- Identifying and defining the problem and resources
- Generating alternative solutions
- Evaluating and selecting best set of solutions
- Preparing for implementation, and evaluating outcomes
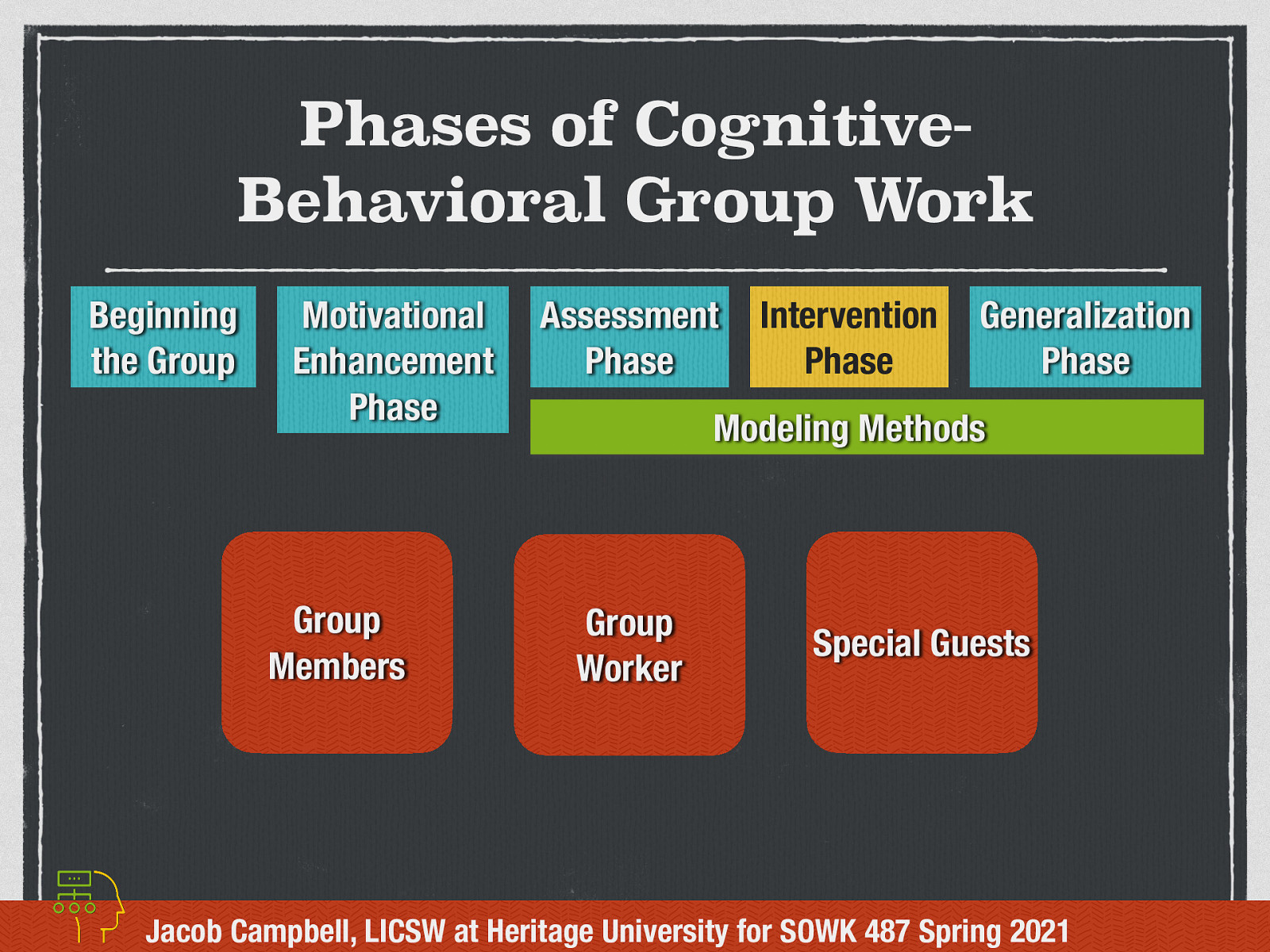
Intervention Phase - Modeling Methods
Modeling Methods is the use of role-plays (simulated demonstrations)
Can be with…
- Group members
- Group worker
- Special guests
[Whole Class Activity] How looks in ART, Debbie’s classroom (social skills school), OSCE (for SW Students)
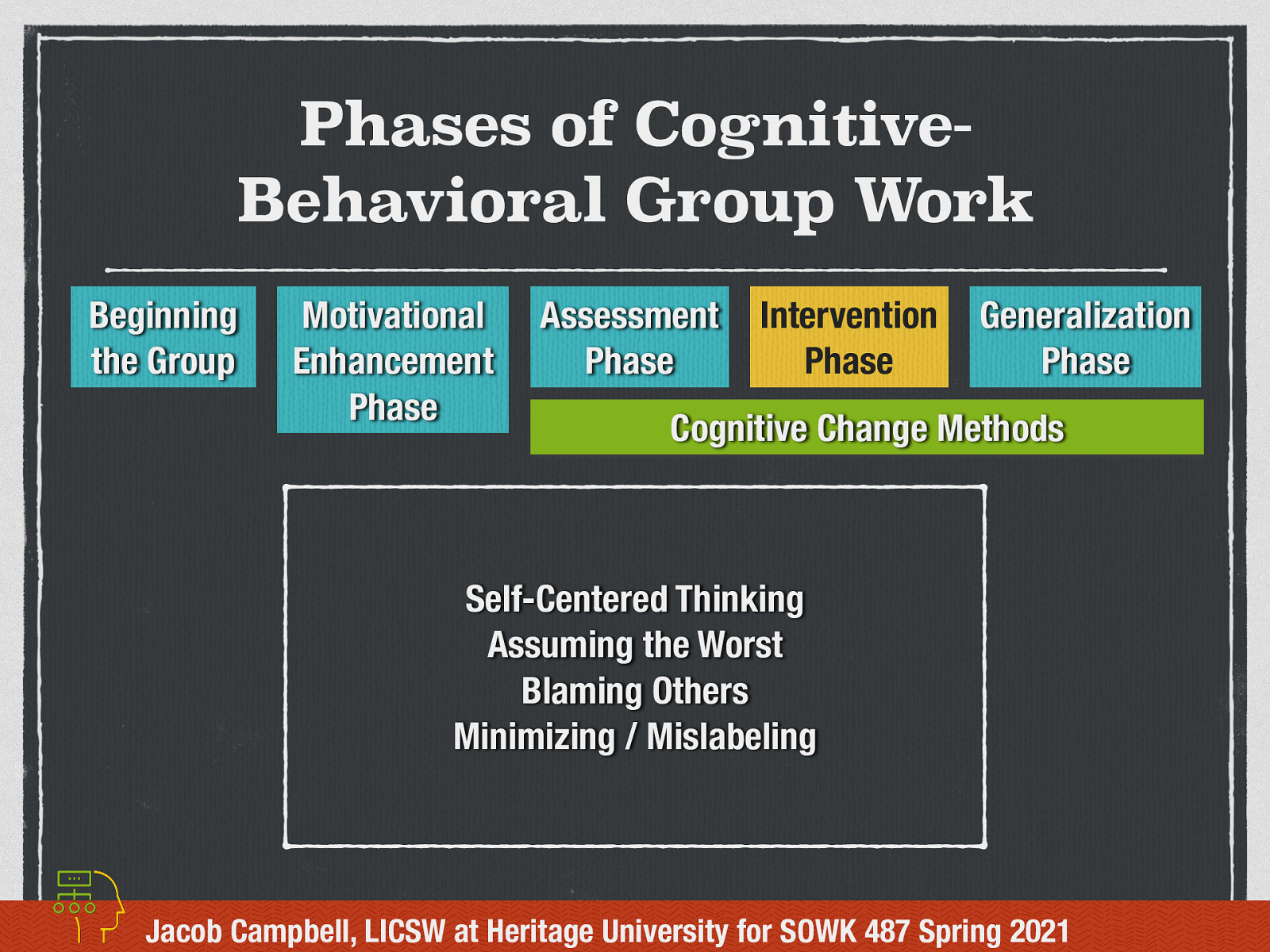
Intervention Phase - Cognitive Change Methods
Cognitive Change Methods is the bulk of types of interventions used in CBGW. The focus is on correcting distorted cognitions and replacing them with coping thoughts. This is oftentimes done through the techniques of cognitive restructuring. In ART, the following are the thought distortions they teach:
Self-centered Thinking: Thinking about only your own needs or interests, not caring about others. One example is saying “If I lie to people, it is nobody’s business but mine.” Assuming the Worst: Acting as if the worst outcome in a situation is the only possible outcome. Thinking people are out to get you. One example is saying, “I might as well lie, people won’t believe me if I tell the truth.” Blaming Others: Not accepting responsibility for your choices and consequences. Making it seem like someone forced you to act how you did. Saying someone else is responsible. One example is saying, “People make me lie when they ask too many questions.” Minimizing/mislabeling: Trying to make something ‘okay’ by making it less than or different from what it really is. One example is saying, “Everybody lies, it’s no big deal.”
Intervention Phase - Community Interventions
Community Interventions is the getting members involved in outside processes such as organizations, volunteering, etc.
-> Think empowerment theory.
Intervention Phase - Other
Some other interventions include…
- Guided Group Exposure: Similar to exposure therapy
- Relaxation Methods: Teaching clients to deal directly with strong emotions such as anxiety, stress, pain, or anger. Might be like
- Operant Methods: Offering positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishments… idea of group reinforcing self as well.
- Relationship Enhancement Methods: Appropriate self-disclosure, humor / personality, effective listening, etc.
- Small-Group Practice Procedures: Broad group participation, role-playing, subgrouping, group exercises.
Generalization Phase
The preparation for transfer of skills to the world.
Often throughout the whole process.

Developing Your Own Curriculum
Developing Your Own Curriculum
What would a group curriculum look like if you were to create one for a therapeutic group?
[Whole Class Activity] Discuss what a group curriculum might look like.
- Objectives
- Planned content
- Short descriptions
- In-depth details
- Verbatim discussion
- Tasks or roles
[Activity] Work with groups of four. Pick a topic for a group. Spend time thinking about what type of curriculum you would do, what parts you would include, and what are some of the information you would do. Plan one of the sessions.

Practice Facilitating a Group
[Activity] Divide up into four groups. Pick one of the group sessions that you previously designed. In shifts of 15 minutes each, rotate through each getting an opportunity to facilitate from where the previous group leader left off.
A cognitive-behavioral framework is a foundation for many therapeutic groups as well as individual clinician’s practices. In an effort to help provide context, during class we will be reviewing several different curricula.
The agenda for this week is as follows:
- Curriculum used with cognitive-behavioral group work
- Phases of the group process
- Implementation of CBGW group
